Excercises
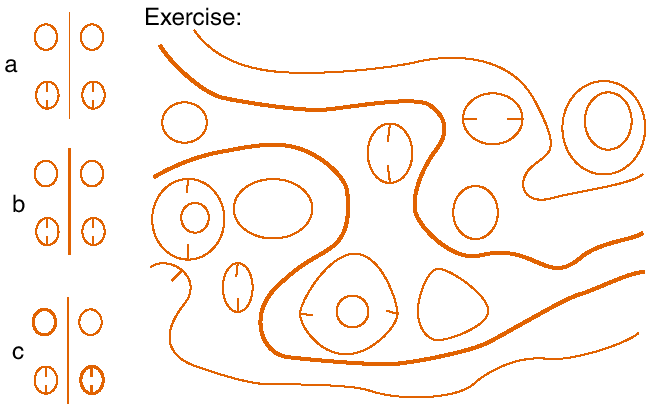
Many orienteers wrongly believe that index contour lines are only required in very hilly areas. Index contour lines provide valuable information in flat areas but first the theory must be understood.
a: The contour line hills and depressions on both sides of the contour can easily be interpreted but it is not possible to find out which hill is a part of a slope and which is a separate hill. One hill must be 2.5 m higher than the other, but which one? The area is flat as only 3 contour lines are indicated.
b: This variant often occurs but is as meaningless as a.
c: Correctly used index contour line having only one possible meaning: the hill on the left is the lower one.
Theory: Crossing a second contour line at the same level means a change of inclination.
Exercise: Redraw the faulty contour line map. The 4 long contours are correct. Some hills and depressions should be index contour lines, but which ones?
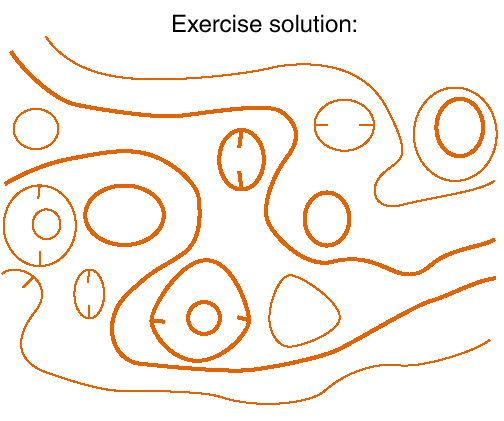
Check the outcome and repeat OHP 43 if necessary. Without understanding the principles it is impossible to correct erroneous maps.